We can present a speaker's words in one of two ways: we can quote them exactly (i.e. Ram claimed to be reading at the time through indirect speech. In this lesson, you will learn how to transition from direct to indirect speech.
The best ways to switch from direct to indirect speech:

Image source: unicusolympiads.com
When the reporting or main verb is in the past tense, all present tenses of the Direct are changed into their corresponding past tenses. It was obliquely said that he was feeling unwell. A continuous present becomes a continuous past. He proclaimed, "My friend is writing letters," etc., that his friend was writing letters. The past perfect transforms from the present perfect. Because the simple past in direct speech is changed to the past perfect in indirect speech, he said, "I have passed the exam."
Rules:
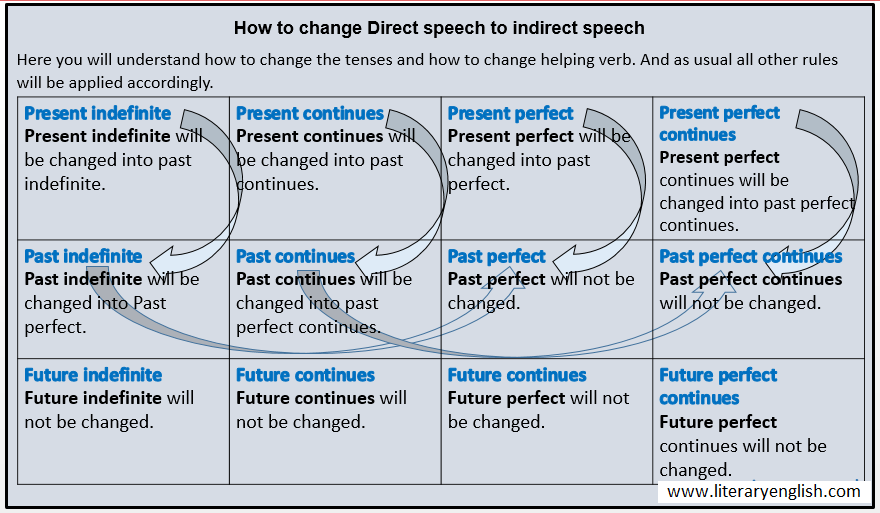
Image Source: actcounsellingandcbtservices.co.uk
In both numbers and persons, a verb must agree with its subject. The proper subject of the verb is replaced with a nearby noun that agrees in number with it. When two or more singular nouns or pronouns are combined, a plural verb is required. While he was reading, I was contemplating how knowledge and wisdom can occasionally be unrelated. If the nouns are the same or refer to the same thing or person, the verb is singular. There, the teaching of Hindi and English emphasized the idea that achieving success requires tenacity and grit. When there are two or more singular subjects, a singular verb is not necessary. The majority of our happiness or sorrow is a result of our own actions, and he doesn't seem to care about praise or blame. When there are several subjects connected by or nor, the verb must also have several parts. Because neither the Chairman nor the Directors are present, the verb should be plural when one of the subjects is joined by or nor is. Both the Chairman and the Directors are not present.
When there is no commonality between the subjects connected by or nor, the verb agrees with the closer. After the words either, neither, each, everyone and many there must be a singular verb. Each boy enjoys reading a lot. Two nouns that are qualified by each or every still require a singular verb even though they are connected by and. Each boy and each girl received an English book.
Some nouns that are plural in form but singular in meaning require a singular verb. Some stories are true.
The sentence structure must be consistent regardless of whether the verb is written as pains or means. Both minor and major pains have been endured. When discussing income, the word "means" always takes a plural verb. He has an abundance of resources.
Twelve dozen were priced at one hundred rupees in the current market. Occasionally, plural nouns with singular meanings require a singular verb.
No takes a plural verb often despite being technically singular. Nobody is more deaf than a person who won't listen. When a noun has a singular form but a plural meaning, such as twelve dozen, which is priced at one hundred rupees at the moment,the plural verb is used.
None frequently takes a plural verb even though it is technically singular. Those who refuse to listen are the deafest. A report from a committee has been made public, the committee is divided over a minor point, and the report has a note.
A plural noun that is a proper name for a single thing or a collection of things, such as The United Nations has a sizable navy, must come before a singular verb.
When a plural noun refers to a particular amount or an amount taken as a whole, the verb is typically singular. For instance, each applicant has 50 minutes to submit their application.
Nouns and Pronouns:

Image source: myenglishlanguage.com
Countable nouns have plural forms and are used with a and an. Examples include books, tables, and flowers. Uncountable nouns that have plural verb forms without the use of a and include a bottle of milk, the surrounding scenery is lovely, and some advice he gave me. For goodness' sake, in a year he will have access to nature's law, the favourite of fortune. Only when two possessive case nouns are close to one another, as in This is my facilitators, the adviser's office, is the apostrophe with added to the last word. When one noun is qualified by two possessive nouns, as in the cases of the Indian king and journey, the complement of the verb to be, when it is expressed by a pronoun, should be in the nominative case. Usually, an objective form is used. The objective form should be used when a pronoun is the subject of a verb or a preposition, as in There is no difference between you and me, let's do it. Whenever a verb comes after, the nominative form is used. He is taller than me despite the fact that we are of equal height. It is expected of every student to complete their assignments and turn in their own work. A pronoun must match its antecedent in person number and gender. Anyone who tries can succeed. At the moment, anyone, everyone, everyone, each, etc . usually have a plural pronoun after them. This is so that the context can determine whether a pronoun is masculine or feminine. For instance, I would be pleased to support each of my students' academic goals. Anyone can succeed if they work hard enough. Always use the definite pronoun one if at all possible. You can never be too cautious with your (not his) reputation, and you have to put your best effort forward if you want to succeed. Depending on what the context requires, neither none nor none is interpreted as either singular or plural. Any weren't in the copy. Any of these terms are no longer in use. Any should be used when referring to more than two people or things. He was the tallest of all of his friends.

